Case Studies

Case Studies
Country: Portugal
Industry: Banking
Profile: Santander occupies a unique position in international banking, with a solid base of recurring business affairs and a high degree of geographical diversification which is guarantee for the future.Santander in 2008 was the third bank in the world by profit, and the seventh by market capitalization.
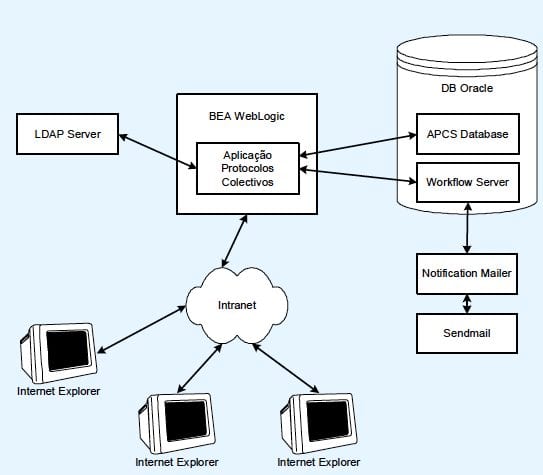
Problem: Santander used several applications based on extraction of relevant documents part of the bank’s branch network, processes for external promoters and Bookmarks Operation Factoring. This information was not centralized and therefore di cult to be consulted.
Solution: Infosistema proposed a solution based on an application developed – iFlow.
Infosistema iFlow is a workflow solution, on which can be mapped and executed business processes.
It is a powerful tool for business process management, which uses the latest standards of BPM technology to provide a simple and intuitive full dematerialization of your business processes.
Santander occupies a unique position in international banking, with a solid base of recurring business affairs and a high degree of geographical diversification which is guarantee for the future. Santander in 2008 was the third bank in the world by profit, and the seventh by market capitalization.
In 2008, theGroup achieved an ordinary attributable profit of 8,876 million, 9% more than in 2007, excluding capital gains
One of the main hallmarks of the Group is its international character, as reflected by the geographic diversification of itsbusiness.
The Bank also has several divisions that operate globally and developing business: Wholesale Banking (Santander Global Banking & Markets), Asset Management (Santander AssetManagement), Insurance (Santander Insurance), Global Private Banking, and Media Payment (Santander Cards).
Santander has built a business model itself, which relies on the following pillars: concentration of activity in retail banking, through the largest branch network among international banks (more than 14,000, including Sovereign), geographic diversification, prudent risk management, cutting edge technology at the service of business efficiency, capital discipline and better management team.
The Bank is thus to provide the greatest added value to its 90 million customers, 3 million shareholders and 170,961 employees.
Santander is committed to society in all countries where it operates. Its main focus within the corporate social responsibility is Santander Universities, which some have more than 700 cooperation agreements with universities around the world.
SANTANDER already used many applications, some not developed by the Informatics team, based on extraction of relevant documents over the network of bank branches, processes for external promoters and Bookmarks Operation Factoring. This information was not centralized, so it was difficult to refer it to the organization, often existed only on paper (material processes) or sent by email or processes into EXCEL files, the databases used were ACCESS. Then there arose a need to take advantage of a platform with workflow functionalities, mainly in order to support the process of receiving and sending letters and the life cycle of purchase invoices (for Business Cards, Stamps and stamp, Orders) from the reception until its accounting and payment. Among the main problems faced with the question Santander include:
Infosistema proposed to Santander a solution based on an application developed – iFlow. The iFlow is a workflow solution, on which can be mapped and executed business processes. The system performs automated routing of information between the various actors in a given process, promoting the early implementation of tasks relating to each of them.
It is a powerful tool for business process management, which uses the latest standards of BPM technology to provide a simple and intuitive full dematerialization of your business processes. It supports a wide range of tasks such as generating forms, fork processes, referral, delegation, validation, integration with enterprise systems, web services and many others.
The iFlow is a workflow system that coordinates the execution of business processes, making the automatic sending of tasks and information relevant to your recipients. The configuration of a flow is performed using an intuitive graphical tool. Stake-holders in each process can complete their tasks through a friendly web interface provided by the system.
The application development is done in an editor that flows similar to what happens with Bank sphere, these objects are already available pre-designed to be programmed or configured as needed.
The technology used in this type of tool is Java, the great advantage of this development is that, no need to write much code, the objects available already meet the diverse needs.
In addition to functions spelled out, there are other features in the Core, such as:
From the standpoint of iFlow, aflow is the mapping of a particular business process and the sequence of computational operations. Each of those operations is modeled in iFlow by a function block. Thus, the definition of a flow is no more than a set of functional blocks connected properly in order to shape certain logic, which can be arbitrarily complex. In turn, a function block is a module (simple and reusable) responsible for performing a specific task (such as validating the value of a variable, run a public database, show a form of user interface, etc.).
Each block has a set of input ports and a set of output ports. It is through these ports that make the connections between the various blocks to form a flow. The Workflow Editor allows, through an intuitive graphical user interface, design the definition of a particular flow, instantiating illustrations of various block and making your call.
The blocks are organized into libraries (toolboxes), according to its functionality.